What Is A Inferior Calcaneal Spur
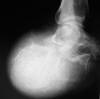
Overview
Heel spurs, or abnormal growths of the heel bone, can cause sharp pains in the heel, especially first thing in the morning and after long periods of rest. In many cases, a heel spur develops as a result of plantar fasciitis, which is the inflammation of the ligament that stretches along the bottom of the foot, from the base of the toes to the heel. In individuals who suffer from plantar fasciitis, the ligament pulls away from the heel as the foot bears weight. In an effort to stabilize the ligament, the body may produce calcium deposits, which can then develop into heel spurs.
Causes
Heel spurs can form as a result of repeated strain placed on foot muscles and ligaments as well as from abnormally stretching the band of tissue connecting the heel and ball of the foot. Repeated injury to the membrane that lines the heel bone can also cause problems as can repeated tight pressure on the back of the heel. The causes can range from excessive walking (especially if unaccustomed to walking), running or jumping to improperly fitted or worn-out shoes. Runners, volleyball players, and tennis players, people who do step aerobics or stair climbing for exercise, those with flat feet, pregnant women, the obese and diabetics and those who wear tight-fitting shoes with a high heel are all prone to developing spurs (and plantar fasciitis) more readily.
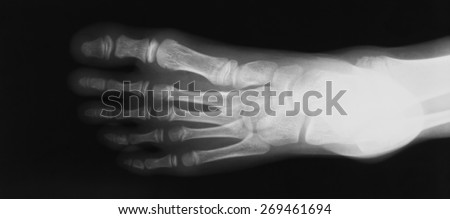
Symptoms
If your body has created calcium build-ups in an effort to support your plantar fascia ligament, each time you step down with your foot, the heel spur is being driven into the soft, fatty tissue which lines the bottom of your heel. Heel spur sufferers experience stabbing sensations because the hard protrusion is literally being jabbed into the heel pad. If left untreated, Plantar Fasciitis and heel spurs can erode the fatty pad of the heel and cause permanent damage to the foot. Fortunately, most cases can be resolved without medications or surgeries.
Diagnosis
The proper diagnosis of a heel spur often requires an X-ray. To make this process as convenient for his patients as possible, most clinics have an on-site digital X-ray and diagnostic ultrasound machines. This can make it unnecessary for patients to visit diagnostic imaging centers, allowing patients to receive more expedient treatment.
Non Surgical Treatment
Heel spurs are considered a self-limited condition, which means that by making small alterations in your lifestyle and regular routines you can often control the condition. The goal is to relieve pain, reduce friction and transfer pressure from your sensitive foot areas. By eliminating the cause of the heel spur and plantar fasciitis (i.e. better shoes, orthotics to fix your gait, losing weight) will help reduce the pressure put on your fascia and heel and can reduce the inflammation caused by your heel spur. Failure to see improvements after conservative treatments may make surgery your only option.
Surgical Treatment
Usually, heel spurs are curable with conservative treatment. If not, heel spurs are curable with surgery, although there is the possibility of them growing back. About 10% of those who continue to see a physician for plantar fascitis have it for more than a year. If there is limited success after approximately one year of conservative treatment, patients are often advised to have surgery.
Prevention
There are heel spur prevention methods available in order to prevent the formation of a heel spur. First, proper footwear is imperative. Old shoes or those that do not fit properly fail to absorb pressure and provide the necessary support. Shoes should provide ample cushioning through the heel and the ball of the foot, while also supporting the arch. Wearing an orthotic shoe insert is one of the best ways to stretch the plantar fascia and prevent conditions such as heel spurs. Stretching the foot and calf is also helpful in preventing damage. Athletes in particular should make sure to stretch prior to any physical activity. Stretching helps prevent heel spurs by making tissue stronger as well as more flexible. In addition, easing into a new or increasingly difficult routine should be done to help avoid strain on the heel and surrounding tissue.